OVERVIEW
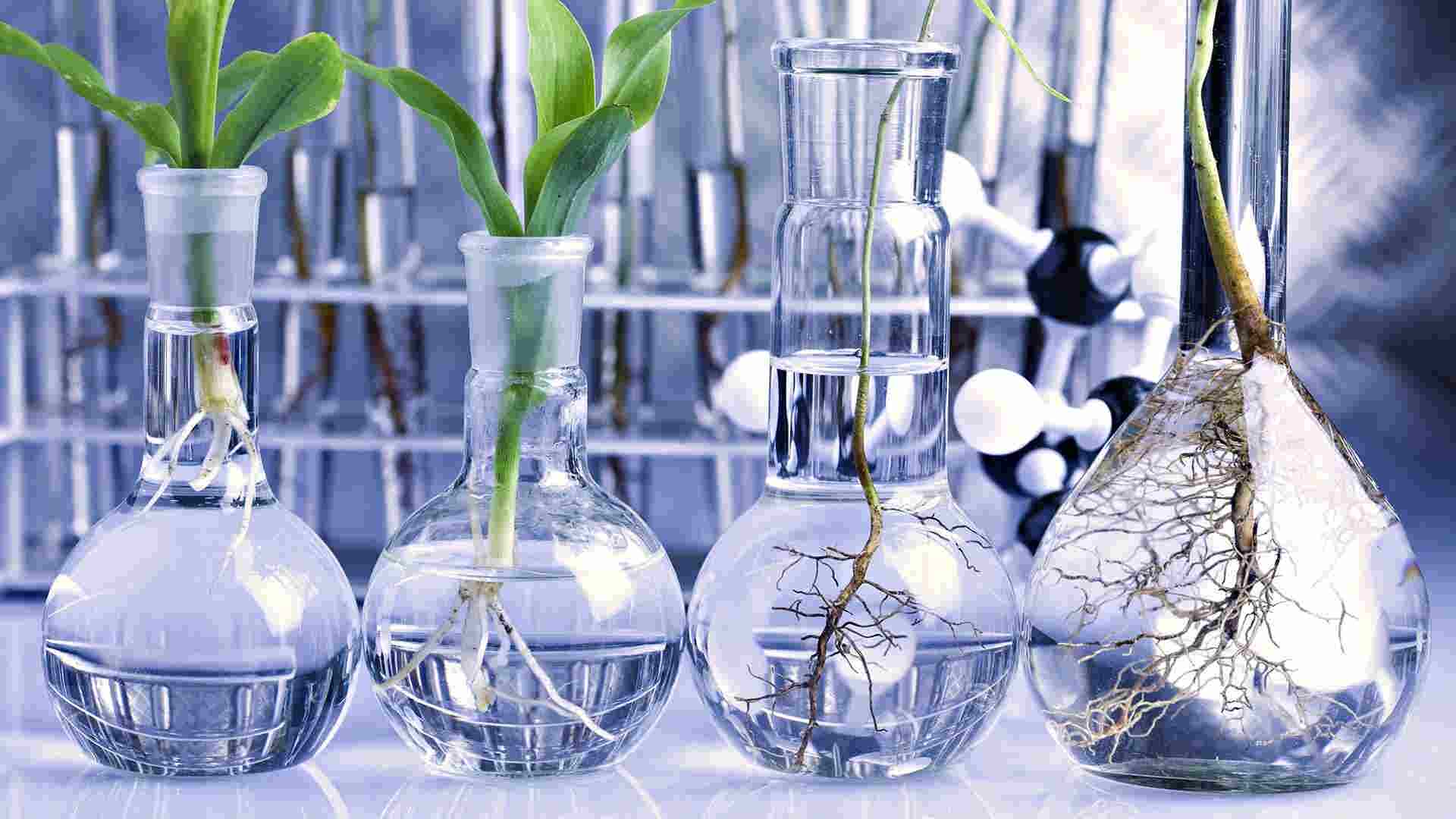
Crop Science is concerned with the application of biological, chemical and physical principles to crops and cropping systems for conversion into food, feed, pharmaceuticals and ornamental commodities. Crop Science examines agronomic crop plants, their growth habits and their genetic improvement.
It also considers the techniques to enhance a plant’s ability to convert sunlight into usable energy, fight off diseases and insects, and produce crops that are economically and environmentally sustainable. In addition to teaching and research, specialists in Crop Science offer their expertise in agrochemical, seed, grain, nursery and food processing companies. Others work as private farmers or professional consultants.
AIMS AND OBJECTIVES
At the end of the programme, students are expected to:
• Demonstrate an understanding of the biology of plants in their environment and the various functions of plants for people and animals, based on such knowledge as plant physiology, morphology and taxonomy, biochemistry, organic and physical chemistry, statistics, plant breeding and genetics.
• Be able to apply the knowledge of the role of natural resources and environmental factors on plant and agro-system development for open and protected plant production systems.
• Demonstrate appreciable knowledge of the importance of ensuring good environment, high food security (quality and quantity) and maintaining biodiversity.
• Ability to work with and solve problems connected to crops, crop production, and environment.
• Ability to collect data (simple measurements in field and laboratory), calculate (simple statistic analysis) and inform about the results.
INDUSTRY/GLOBAL TRENDS
On a global scale, the production of adequate and accessible food is a considerable challenge. Aside cropping system and technology, environment and climate concerns also limit crop production in many areas. Research and innovation is therefore a constant area of focus in Crop Science. Recent innovations involve biotechnology and production of bio-fuels.
Biotechnology is being used to manipulate the genetic material of plants and crops, attempting to make them more productive or resistant to disease. Bio-fuels are manufactured from agricultural derivatives such as turning crops into energy sources. A typical example is ethanol, produced from maize.
ASSESSMENT
Students are assessed through a combination of assignments, examinations and projects.
TUITION METHODS
Lectures, class discussion and practical tutorials.
CAREER PROSPECTS
Career opportunities in Crop Science include the under listed:
• Agronomist
• Crop Breeder/Biochemist
• Chemical/Fertiliser Specialist
• Crop Production Specialists/ Manager
• Crop Marketing Specialist/ Manager
• Extension Agent
• Seed Production Specialist/ Technologist
• Weed Scientist